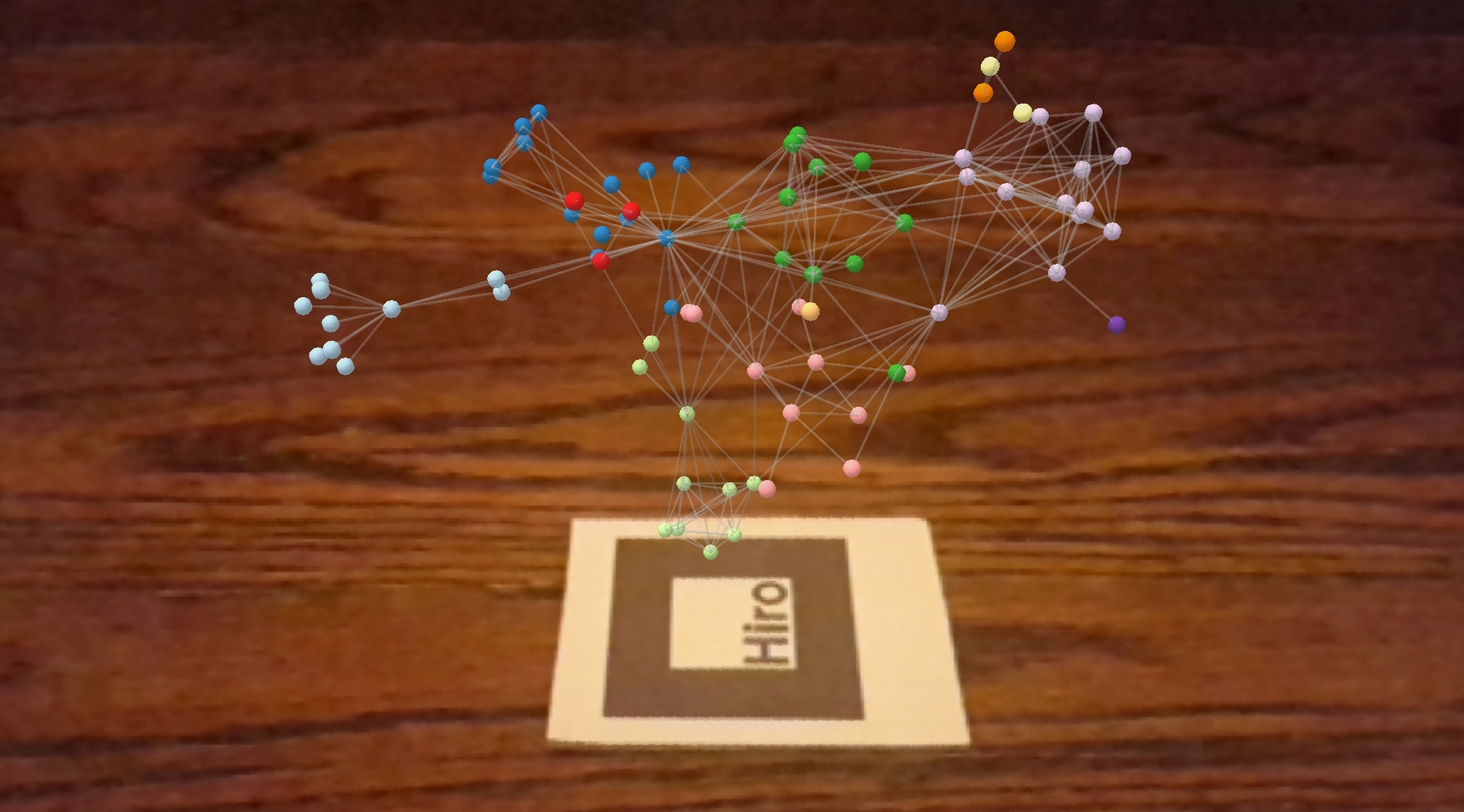
3D Force-Directed Graph in AR
A web component to represent a graph data structure in augmented reality using a force-directed iterative layout. Uses AR.js with A-Frame for rendering and d3-force-3d for the layout physics engine.
See also the VR version, WebGL 3D version, and the A-Frame component version (aframe-forcegraph-component).
And check out the React bindings.
To load any of the examples below:
- Open this hiro marker image in your desktop browser.
- Open the example on your phone browser, and point it at your desktop screen.
Check out the examples:
- Basic (source)
- Asynchronous load (source)
- Larger graph (~4k elements) (source)
- Directional arrows (source)
- Directional moving particles (source)
- Curved lines and self links (source)
- Auto-colored nodes/links (source)
- Text as nodes (source)
- Images as nodes (source)
- Custom node geometries (source)
- Text in links (source)
- Dynamic data changes (source)
- Node collision detection (source)
- Emit link particles on demand (source)
❤️ Support This Project
If you find this module useful and would like to support its development, you can buy me a ☕. Your contributions help keep open-source sustainable!

Quick start
import ForceGraphAR from '3d-force-graph-ar';
or using a script tag
<script src="//cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/3d-force-graph-ar"></script>
then
const myGraph = new ForceGraphAR(<myDOMElement>)
.graphData(<myData>);
Make sure to load these two script tags in your application, required for AR.js + A-frame to function properly:
<script src="//cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/aframe"></script>
<script src="//cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@ar-js-org/ar.js"></script>
API reference
Initialisation
new ForceGraphAR(<domElement>, { configOptions })
| Config options | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| markerAttrs: object | Set of attributes that define the marker where the force directed graph is mounted, according to the a-marker specification. | { preset: 'hiro' } |
Data input
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| graphData([data]) | Getter/setter for graph data structure (see below for syntax details). | { nodes: [], links: [] } |
| jsonUrl([url]) | URL of JSON file to load graph data directly from, as an alternative to specifying graphData directly. | |
| nodeId([str]) | Node object accessor attribute for unique node id (used in link objects source/target). | id |
| linkSource([str]) | Link object accessor attribute referring to id of source node. | source |
| linkTarget([str]) | Link object accessor attribute referring to id of target node. | target |
Container layout
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| yOffset([number]) | Getter/setter for the offset distance above the marker where to place the center coordinates <0,0,0> of the force directed graph. Measured in terms of marker width units. |
1.5 |
| glScale([number]) | Getter/setter for the translation scale between real world distances and WebGL units, determining the overall size of the graph. Defined in terms of how many GL units fit in a full marker width. | 200 |
| width([px]) | Getter/setter for the viewport canvas width. | <window width> |
| height([px]) | Getter/setter for the viewport canvas height. | <window height> |
Node styling
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| nodeRelSize([num]) | Getter/setter for the ratio of node sphere volume (cubic px) per value unit. | 4 |
| nodeVal([num, str or fn]) | Node object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the node numeric value (affects sphere volume). | val |
| nodeVisibility([boolean, str or fn]) | Node object accessor function, attribute or a boolean constant for whether to display the node. | true |
| nodeColor([str or fn]) | Node object accessor function or attribute for node color (affects sphere color). | color |
| nodeAutoColorBy([str or fn]) | Node object accessor function (fn(node)) or attribute (e.g. 'type') to automatically group colors by. Only affects nodes without a color attribute. |
|
| nodeOpacity([num]) | Getter/setter for the nodes sphere opacity, between [0,1]. | 0.75 |
| nodeResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the geometric resolution of each node, expressed in how many slice segments to divide the circumference. Higher values yield smoother spheres. | 8 |
| nodeThreeObject([Object3d, str or fn]) | Node object accessor function or attribute for generating a custom 3d object to render as graph nodes. Should return an instance of ThreeJS Object3d. If a falsy value is returned, the default 3d object type will be used instead for that node. | default node object is a sphere, sized according to val and styled according to color. |
| nodeThreeObjectExtend([bool, str or fn]) | Node object accessor function, attribute or a boolean value for whether to replace the default node when using a custom nodeThreeObject (false) or to extend it (true). |
false |
Link styling
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| linkVisibility([boolean, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a boolean constant for whether to display the link line. A value of false maintains the link force without rendering it. |
true |
| linkColor([str or fn]) | Link object accessor function or attribute for line color. | color |
| linkAutoColorBy([str or fn]) | Link object accessor function (fn(link)) or attribute (e.g. 'type') to automatically group colors by. Only affects links without a color attribute. |
|
| linkOpacity([num]) | Getter/setter for line opacity of links, between [0,1]. | 0.2 |
| linkWidth([num, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the link line width. A value of zero will render a ThreeJS Line whose width is constant (1px) regardless of distance. Values are rounded to the nearest decimal for indexing purposes. |
0 |
| linkResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the geometric resolution of each link, expressed in how many radial segments to divide the cylinder. Higher values yield smoother cylinders. Applicable only to links with positive width. | 6 |
| linkCurvature([num, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the curvature radius of the link line. Curved lines are represented as 3D bezier curves, and any numeric value is accepted. A value of 0 renders a straight line. 1 indicates a radius equal to half of the line length, causing the curve to approximate a semi-circle. For self-referencing links (source equal to target) the curve is represented as a loop around the node, with length proportional to the curvature value. Lines are curved clockwise for positive values, and counter-clockwise for negative values. Note that rendering curved lines is purely a visual effect and does not affect the behavior of the underlying forces. |
0 |
| linkCurveRotation([num, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the rotation along the line axis to apply to the curve. Has no effect on straight lines. At 0 rotation, the curve is oriented in the direction of the intersection with the XY plane. The rotation angle (in radians) will rotate the curved line clockwise around the “start-to-end” axis from this reference orientation. |
0 |
| linkMaterial([Material, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function or attribute for specifying a custom material to style the graph links with. Should return an instance of ThreeJS Material. If a falsy value is returned, the default material will be used instead for that link. | default link material is MeshLambertMaterial styled according to color and opacity. |
| linkThreeObject([Object3d, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function or attribute for generating a custom 3d object to render as graph links. Should return an instance of ThreeJS Object3d. If a falsy value is returned, the default 3d object type will be used instead for that link. | default link object is a line or cylinder, sized according to width and styled according to material. |
| linkThreeObjectExtend([bool, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a boolean value for whether to replace the default link when using a custom linkThreeObject (false) or to extend it (true). |
false |
| linkPositionUpdate([fn(linkObject, { start, end }, link)]) | Getter/setter for the custom function to call for updating the position of links at every render iteration. It receives the respective link ThreeJS Object3d, the start and end coordinates of the link ({x,y,z} each), and the link’s data. If the function returns a truthy value, the regular position update function will not run for that link. |
|
| linkDirectionalArrowLength([num, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the arrow head indicating the link directionality. The arrow is displayed directly over the link line, and points in the direction of source > target. A value of 0 hides the arrow. |
0 |
| linkDirectionalArrowColor([str or fn]) | Link object accessor function or attribute for the color of the arrow head. | color |
| linkDirectionalArrowRelPos([num, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the longitudinal position of the arrow head along the link line, expressed as a ratio between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates immediately next to the source node, 1 next to the target node, and 0.5 right in the middle. |
0.5 |
| linkDirectionalArrowResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the geometric resolution of the arrow head, expressed in how many slice segments to divide the cone base circumference. Higher values yield smoother arrows. | 8 |
| linkDirectionalParticles([num, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the number of particles (small spheres) to display over the link line. The particles are distributed equi-spaced along the line, travel in the direction source > target, and can be used to indicate link directionality. |
0 |
| linkDirectionalParticleSpeed([num, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the directional particles speed, expressed as the ratio of the link length to travel per frame. Values above 0.5 are discouraged. |
0.01 |
| linkDirectionalParticleOffset([num, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the offset of the directional particles initial position, expressed as a value between 0 and 1, relative to a full position cycle. | 0 |
| linkDirectionalParticleWidth([num, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the directional particles width. Values are rounded to the nearest decimal for indexing purposes. | 0.5 |
| linkDirectionalParticleColor([str or fn]) | Link object accessor function or attribute for the directional particles color. | color |
| linkDirectionalParticleResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the geometric resolution of each directional particle, expressed in how many slice segments to divide the circumference. Higher values yield smoother particles. | 4 |
| linkDirectionalParticleThreeObject([Object3d, str or fn]) | Link object accessor function or attribute for a custom 3d object to use in the directional particles. Should return an instance of ThreeJS Object3d. Activating this will ignore the set values for the particle’s width, color and resolution. | |
| emitParticle(link) | An alternative mechanism for generating particles, this method emits a non-cyclical single particle within a specific link. The emitted particle shares the styling (speed, shape, color) of the regular particle props. A valid link object that is included in graphData should be passed as a single parameter. |
Interaction
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| onNodeHover([fn]) | Callback function for node hover events. The node object (or null if there’s no node directly under the pointer line of sight) is included as the first argument, and the previous node object (or null) as second argument. |
- |
| onLinkHover([fn]) | Callback function for link hover events. The link object (or null if there’s no link directly under the pointer line of sight) is included as the first argument, and the previous link object (or null) as second argument. |
- |
| onNodeClick([fn]) | Callback function for node click events. The node object is included as sole argument. | - |
| onLinkClick([fn]) | Callback function for link click events. The link object is included as sole argument. | - |
Force engine configuration
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| forceEngine([str]) | Getter/setter for which force-simulation engine to use (d3 or ngraph). | d3 |
| numDimensions([int]) | Getter/setter for number of dimensions to run the force simulation on (1, 2 or 3). | 3 |
| dagMode([str]) | Apply layout constraints based on the graph directionality. Only works correctly for DAG graph structures (without cycles). Choice between td (top-down), bu (bottom-up), lr (left-to-right), rl (right-to-left), zout (near-to-far), zin (far-to-near), radialout (outwards-radially) or radialin (inwards-radially). |
|
| dagLevelDistance([num]) | If dagMode is engaged, this specifies the distance between the different graph depths. |
auto-derived from the number of nodes |
| dagNodeFilter([fn]) | Node accessor function to specify nodes to ignore during the DAG layout processing. This accessor method receives a node object and should return a boolean value indicating whether the node is to be included. Excluded nodes will be left unconstrained and free to move in any direction. |
node => true |
| onDagError([fn]) | Callback to invoke if a cycle is encountered while processing the data structure for a DAG layout. The loop segment of the graph is included for information, as an array of node ids. By default an exception will be thrown whenever a loop is encountered. You can override this method to handle this case externally and allow the graph to continue the DAG processing. Strict graph directionality is not guaranteed if a loop is encountered and the result is a best effort to establish a hierarchy. | throws exception |
| d3AlphaMin([num]) | Getter/setter for the simulation alpha min parameter, only applicable if using the d3 simulation engine. | 0 |
| d3AlphaDecay([num]) | Getter/setter for the simulation intensity decay parameter, only applicable if using the d3 simulation engine. | 0.0228 |
| d3VelocityDecay([num]) | Getter/setter for the nodes’ velocity decay that simulates the medium resistance, only applicable if using the d3 simulation engine. | 0.4 |
| d3Force(str, [fn]) | Getter/setter for the internal forces that control the d3 simulation engine. Follows the same interface as d3-force-3d’s simulation.force. Three forces are included by default: 'link' (based on forceLink), 'charge' (based on forceManyBody) and 'center' (based on forceCenter). Each of these forces can be reconfigured, or new forces can be added to the system. This method is only applicable if using the d3 simulation engine. |
|
| d3ReheatSimulation() | Reheats the force simulation engine, by setting the alpha value to 1. Only applicable if using the d3 simulation engine. |
|
| ngraphPhysics([object]) | Specify custom physics configuration for ngraph, according to its configuration object syntax. This method is only applicable if using the ngraph simulation engine. | ngraph default |
| warmupTicks([int]) | Getter/setter for number of layout engine cycles to dry-run at ignition before starting to render. | 0 |
| cooldownTicks([int]) | Getter/setter for how many build-in frames to render before stopping and freezing the layout engine. | Infinity |
| cooldownTime([num]) | Getter/setter for how long (ms) to render for before stopping and freezing the layout engine. | 15000 |
| onEngineTick(fn) | Callback function invoked at every tick of the simulation engine. | - |
| onEngineStop(fn) | Callback function invoked when the simulation engine stops and the layout is frozen. | - |
| refresh() | Redraws all the nodes/links. |
Utility
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| getGraphBbox([nodeFilterFn]) | Returns the current bounding box of the nodes in the graph, formatted as { x: [<num>, <num>], y: [<num>, <num>], z: [<num>, <num>] }. If no nodes are found, returns null. Accepts an optional argument to define a custom node filter: node => <boolean>, which should return a truthy value if the node is to be included. This can be useful to calculate the bounding box of a portion of the graph. |
Input JSON syntax
{
"nodes": [
{
"id": "id1",
"name": "name1",
"val": 1
},
{
"id": "id2",
"name": "name2",
"val": 10
},
...
],
"links": [
{
"source": "id1",
"target": "id2"
},
...
]
}